-
BAY-Y-3118游离碱
- names:
BAY-Y 3118
- CAS号:
151213-16-0
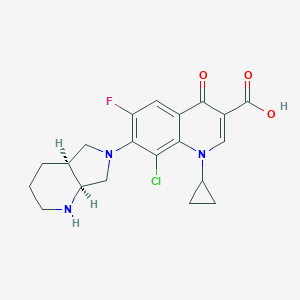
MDL Number: MFCD31557930 - MF(分子式): C20H21ClFN3O3 MW(分子量): 405.85
- EINECS: Reaxys Number:
- Pubchem ID:119375 Brand:BIOFOUNT
| 货品编码 | 规格 | 纯度 | 价格 (¥) | 现价(¥) | 特价(¥) | 库存描述 | 数量 | 总计 (¥) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YZM000210-100mg | 100mg | >97% | ¥ 0.00 | ¥ 0.00 | 1-3days | ¥ 0.00 |
| 中文别名 | BAY-Y-3118游离碱(151213-16-0);Bay y 3118;Bay Y3118;Bay-Y3118;1-环丙基-7-(2,8-二氮杂双环(4.3.0)非-8-基)-6-氟-8-氯-1,4-二氢-4-氧代-3-喹啉羧酸盐酸盐; 7-[(4aS,7aS)-1,2,3,4,4a,5,7,7a-八氢吡咯并[3,4-b]吡啶-6-基] -8-氯-1-环丙基-6-氟-4-氧代喹啉-3-羧酸; 1-环丙基-7-(2,8-二氮杂双环(4.3.0)非-8-基)-6-氟-8-氯-1,4-二氢-4-氧代-3-喹啉羧酸盐酸盐; |
| 英文别名 | BAY-Y 3118(151213-16-0);1-cyclopropyl-7-(2,8-diazabicyclo(4.3.0)non-8-yl)-6-fluoro-8-chloro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid hydrochloride;Bay y 3118;Bay Y3118;Bay-Y3118; 7-[(4aS,7aS)-1,2,3,4,4a,5,7,7a-octahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl]-8-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; 1-cyclopropyl-7-(2,8-diazabicyclo(4.3.0)non-8-yl)-6-fluoro-8-chloro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid hydrochloride; |
| CAS号 | 151213-16-0 |
| Inchi | InChI=1S/C20H21ClFN3O3/c21-16-17-12(19(26)13(20(27)28)8-25(17)11-3-4-11)6-14(22)18(16)24-7-10-2-1-5-23-15(10)9-24/h6,8,10-11,15,23H,1-5,7,9H2,(H,27,28)/t10-,15+/m0/s1 |
| InchiKey | VRXORHRXNRJZCQ-ZUZCIYMTSA-N |
| 分子式 Formula | C20H21ClFN3O3 |
| 分子量 Molecular Weight | 405.85 |
| 溶解度Solubility | |
| 性状 | Solid |
| 储藏条件 Storage conditions | Store in a cool and dry place |
BAY-Y-3118游离碱(151213-16-0,BAY-Y 3118)实验注意事项:
1.实验前需戴好防护眼镜,穿戴防护服和口罩,佩戴手套,避免与皮肤接触。
2.实验过程中如遇到有毒或者刺激性物质及有害物质产生,必要时实验操作需要手套箱内完成以免对实验人员造成伤害
3.实验后产生的废弃物需分类存储,并交于专业生物废气物处理公司处理,以免造成环境污染Experimental considerations:
1. Wear protective glasses, protective clothing and masks, gloves, and avoid contact with the skin during the experiment.
2. The waste generated after the experiment needs to be stored separately, and handed over to a professional biological waste gas treatment company to avoid environmental pollution.
Tags:BAY-Y 3118试剂,BAY-Y 3118杂质,BAY-Y 3118中间体,BAY-Y 3118合成,BAY-Y 3118密度,BAY-Y 3118溶解度,BAY-Y 3118旋光度,BAY-Y 3118闪点,BAY-Y 3118熔点,BAY-Y 3118购买,

| 产品说明 | BAY-Y-3118游离碱(151213-16-0,BAY-Y 3118)是一种具有抗菌活性的新型氯氟喹诺酮。 |
| Introduction | BAY-Y-3118游离碱(151213-16-0,BAY-Y 3118) is a new chlorof luoroquinolone with antimicrobial activity. |
| Application1 | |
| Application2 | |
| Application3 |
BAY-Y-3118游离碱(151213-16-0,BAY-Y 3118)药理学:
BAY-Y 3118是一种4-喹诺酮,对革兰氏阴性和革兰氏阳性病原体以及厌氧菌和细胞内细菌均具有出色的抗菌活性,可能对抗感染治疗的发展做出重要贡献。
BAY-Y 3118对流感嗜血杆菌,卡莫拉莫拉杆菌,鲍曼不动杆菌,麦芽黄单胞菌,革兰氏阳性球菌和厌氧菌有效;50%o的MIC(MIC50s)和MIC90s分别为≤0.015和≤0.015,≤0.015和≤0.015、0.03和2、0.25和0.5、0.06和1、0.12和0.25μg/ mL[1]。在2-100 mg / L的细胞外浓度下,BAY-Y 3118的细胞浓度与细胞外浓度之比高于6.3。BAY-Y 3118的吸收迅速,可逆且不饱和。BAY-Y 3118的细胞内渗透受环境温度和细胞生存力的显着影响。BAY-Y 3118在人多形核白细胞(PMN)中达到较高的细胞内浓度,并在细胞内保持活性[2]。单核细胞增生李斯特氏菌和其他李斯特菌属的所有菌株。高度易感;这些生物的MIC范围为0.062至0.25μg/ mL。BAY-Y 3118 在体外具有快速杀菌作用,在去除抗生素后3小时内会产生抗生素后作用。单核细胞增生李斯特氏菌已从用BAY-Y 3118处理的受感染L929细胞中消除,表明对这些细胞中的李斯特菌具有杀菌作用。
| 警示图 | |
| 危险性 | warning |
| 危险性警示 | Not available |
| 安全声明 | H303吞入可能有害+H313皮肤接触可能有害+H2413吸入可能对身体有害 |
| 安全防护 | P264处理后彻底清洗+P280戴防护手套/穿防护服/戴防护眼罩/戴防护面具+P305如果进入眼睛+P351用水小心冲洗几分钟+P338取出隐形眼镜(如果有)并且易于操作,继续冲洗+P337如果眼睛刺激持续+P2393获得医疗建议/护理 |
| 备注 | 实验过程中防止吸入、食入,做好安全防护 |
| Fass RJ, et al. In vitro activity of Bay y 3118, a new quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Nov;37(11):2348-57. |
| García I, et al. Intracellular penetration and activity of BAY Y 3118 in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Oct;38(10):2426-9. |
| Nichterlein T, et al. Bay Y 3118, a new quinolone derivative, rapidly eradicates Listeria monocytogenes from infected mice and L929 cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Jul;38(7):1501-6. |
| Isolation of two subpopulations of Mycobacterium avium within human macrophages FEMS microbiology letters,10483718 1999-09-01 |
| Development of a firefly luciferase-based assay for determining antimicrobial susceptibility of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis Journal of clinical microbiology,9889208 1999-02-01 |
1、Damage to mitochondrial DNA induced by the quinolone Bay y 3118 in embryonic turkey liver
H Enzmann 1, C Wiemann, H J Ahr, G Schlüter
Abstract Quinolones are a class of antibiotics that induce damage to and loss of DNA from bacteria. The structural organization of bacterial DNA is more similar to eukaryotic mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) than to eukaryotic chromosomal or nuclear DNA (nDNA). Antibiotics affecting the bacterial genome may therefore preferentially damage mtDNA rather than nDNA. We investigated the effect of a quinolone on mtDNA in avian embryonic hepatocytes in ovo. The quinolone Bay y 3118 (1-cyclopropyl-7-(2,8-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-8-yl) 6-fluoro-8-chloro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid hydrochloride, chemical structure see Bremm et al. [K.D. Bremm, U. Petersen, K.G. Metzger, R. Endermann, In vitro evaluation of Bay-y 3118, a new full-spectrum fluoroquinolone, Chemotherapy 38 (1992) 376-387] was injected into fertilized turkey eggs 8 days before hatching at doses of 1, 3, 10 and 30 mg per egg. The embryos were removed from the eggs after 4 days and liver samples were shock frozen. Mitochondrial DNA was purified from samples of the embryonic liver. The integrity of mtDNA was investigated by electrophoresis on agarose gels with native mtDNA and with ribonuclease-treated mtDNA. Fluorescent staining of the electrophoresis gels allows the densitometric quantification of the mtDNA of the regular band at 16 kilobases (kb) and the amount of DNA fragments of irregular size (smear). The genotoxic nitrosamine nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA) has previously been shown to reduce the content of mtDNA of the regular size of 16 kb and to induce the occurrence of smaller fragments of mtDNA [H. Enzmann, C. Kühlem, E. Löser, P. Bannasch, Damage to mitochondrial DNA induced by the hepatocarcinogen, diethylnitrosamine in ovo, Mutation Res. 329 (1995) 113-120]. After exposure to 10 and 30 mg Bay y 3118, a dose-dependent induction of damage to the mtDNA was found, whereas exposure to 3 and 1 mg showed no effect. NDEA (25 mg) was used as positive control. Testing chemical compounds in the in ovo model is a simple and rapid approach for investigations on chemically induced alterations of mtDNA.
2、Real-time visualization of photochemically induced fluorescence of 8-halogenated quinolones: lomefloxacin, clinafloxacin and Bay3118 in live human HaCaT keratinocytes
Edmond B Koker 1, Piotr J Bilski, Ann G Motten, Baozhong Zhao, Colin F Chignell, Yu-Ying He
Abstract Halogenoquinolones are potent and widely used antimicrobials blocking microbial DNA synthesis. However, they induce adverse photoresponses through the absorption of UV light, including phototoxicity and photocarcinogenicity. The phototoxic responses may be the result of photosensitization of singlet oxygen, production of free radicals and/or other reactive species resulting from photodehalogenation. Here, we report the use of laser scanning confocal microscopy to detect and to follow the fluorescence changes of one monohalogenated and three di-halogenated quinolones in live human epidermal keratinocyte cells during in situ irradiation by confocal laser in real time. Fluorescence image analysis and co-staining with the LysoTracker probe showed that lysosomes are a preferential site of drug localization and phototransformations. As the lysosomal environment is relatively acidic, we also determined how low pH may affect the dehalogenation and concomitant fluorescence. With continued UV irradiation, fluorescence increased in the photoproducts from BAY y3118 and clinafloxacin, whereas it decreased for lomefloxacin and moxifloxacin. Our images not only help to localize these phototoxic agents in the cell, but also provide means for dynamic monitoring of their phototransformations in the cellular environment.
3、Fluoroquinolones as chemical tools to define a strategy for photogenotoxicity in vitro assessment
L Marrot 1, J P Belaidi, C Chaubo, J R Meunier, P Perez, C Agapakis-Causse
Abstract Today's lifestyle is often associated with frequent exposure to sunlight, but some xenobiotics used in drugs, cosmetics or food chemicals can produce adverse biological effects when irradiated. In particular, they can increase the risk of photogenotoxicity already due to UV radiation itself. There is thus a need to design appropriate approaches in order to obtain relevant data at the molecular and cellular level in this field. For ethical and practical reasons, in vitro models can be very convenient at least for first evaluation tests. Here, we propose a strategy based on complementary experiments to study the photogenotoxic potential of a compound. The fluoroquinolones BAYy3118 and lomefloxacin were used as standards to demonstrate the performance of each test: photoinduced interaction with supercoiled circular DNA, photomutagenicity in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisae, induction of DNA photodamage in cultured human skin cells as revealed by comet assay, and finally induction of specific phototoxic stress responses such as p53 activation or melanogenesis stimulation. Such a strategy should help to ensure the safety of products likely to undergo environmental sunlight exposure.
4、Comparative in vitro and in vivo activity of the C-8 methoxy quinolone moxifloxacin and the C-8 chlorine quinolone BAY y 3118 A Dalhoff 1 Abstract The C-8 methoxy quinolone moxifloxacin is highly bactericidal against wild-type and first-step gyrase- and topoisomerase IV-resistant mutants. This finding led to the hypothesis that the C-8 methoxy group may lower the propensity for resistance development compared with quinolones possessing different substituents at the C-8 position. Therefore, resistance development of the C-8 methoxy quinolone moxifloxacin was compared with that of its structural analogue BAY y 3118 (chlorine moiety at the C-8 position), with Staphylococcus aureus used as the test organism. The spontaneous emergence of resistance was quantified by counting the number of colonies growing on drug-free medium compared with moxifloxacin- or BAY y 3118-containing media. The multistep emergence of quinolone resistance was encountered by growing S. aureus over 8 passages in drug-containing medium. Human serum concentrations were simulated in an in vitro model over 84 h (dosing every 24 h), and total and resistant S. aureus were quantified. Spontaneous mutation frequencies of 6x10-11 for moxifloxacin and 4x10-7 for BAY y 3118 were observed. Multistep resistance to moxifloxacin developed slowly (2-fold rise) but rapidly against BAY y 3118 (>16-fold rise). No resistance against moxifloxacin developed in this model, whereas resistance to BAY y 3118 began to develop after 4 h. Thus, as the C-8 moiety was the only difference, the 8-methoxy group on moxifloxacin appeared to significantly lower the propensity for quinolone resistance development.
- 相关产品
-
< >
- 推荐产品
-
< >
- 最新产品
-
< >
新闻
怎么做细胞爬片免疫组化染色实验
细胞爬片免疫组化染色,是通过细胞爬片是让玻片浸在细胞培养基内,细胞在玻片上生长,主要用于组织学,免疫组织化学...
2020/7/20 22:04:33
提取病毒RNA的实验方法
提取病毒RNA方法分别有:异硫氰酸胍的提取病毒RNA方法、TRIzol LS提取法、Trizol法提取法等等...
2020/7/22 20:29:26

chelex 100树脂国产替代之路-BIOFOUNT范德生物
Chelex 100螯合离子交换树脂对铜、铁和其他重金属?的偏好显著高于对钠、钾等一价阳离子的偏好。它对二价...
2025/11/4 14:22:46

9月开学季——助研新学期 范德送好礼
2025/8/28 15:30:55

Waxfilm 实验室封口膜:技术与国际市场的双重突破
在实验室耗材领域,封口膜是保障实验准确性与稳定性的关键产品之一。近年来,Waxfilm?实验室封口膜凭借其卓...
2025/5/13 13:03:40

Waxfilm实验室封口膜的5大突破
Waxfilm实验室封口膜作为生物功能膜领域的国产技术突破和品牌突破,是生物领域中国技术发展的缩影。
2025/5/6 17:02:07
各种微流控芯片键合方法的优缺点
微流控芯片键合:目前主要有激光焊接、热压键合、胶键合、超音波焊接,每种方法都有各自的优缺点。本文主要介绍聚酯...
2023/7/28 10:43:09

新一代微流控键合解决方案
微流控键合解决方案:微流控芯片制造的一个重要环节,也是最容易被忽视的--芯片键合。其中一个重要因素是:微流控...
2023/7/27 12:44:28
荧光素钾盐使用说明
D-荧光素钾盐(K+)设计用于体外和体内生物发光测定。D-荧光素的质量和纯度对于获得良好和可重复的结果至关重...
2023/7/20 11:05:11
如何选BSA(牛血清白蛋白)
如何选BSA(牛血清白蛋白):牛血清白蛋白(BSA)有多种形式,如何选择适合自己的牛血清白蛋白(BSA)是一...
2023/2/14 13:09:18




 购物车
购物车 



