-
PknG抑制剂
- names:
AX20017
- CAS号:
329221-38-7
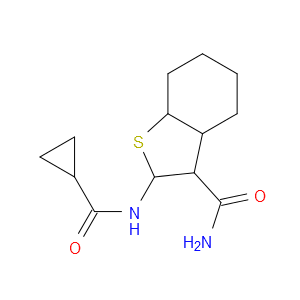
MDL Number: MFCD00785286 - MF(分子式): C13H16N2O2S MW(分子量): 264.34
- EINECS: Reaxys Number:
- Pubchem ID:673481 Brand:BIOFOUNT
PknG抑制剂(AX20017,329221-38-7)是蛋白激酶G(PknG)的小分子抑制剂,IC50:0.39μM(PknG)。
| 货品编码 | 规格 | 纯度 | 价格 (¥) | 现价(¥) | 特价(¥) | 库存描述 | 数量 | 总计 (¥) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YZM000167-5mg | 5mg | 99.95% | ¥ 682.50 | ¥ 682.50 | 2-3天 | ¥ 0.00 |
| 中文别名 | PknG抑制剂(329221-38-7);AX 20017;AX-20017;AX20017; |
| 英文别名 | AX20017(329221-38-7);AX 20017;AX-20017;AX20017;AX 20017;PknG Inhibitor;2-(cyclopropanecarboxamido)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxamide;AX-20017; AX 20017; Mycobacterial Protein Kinase G Inhibitor; 2-(Cyclopropanecarbonylamino)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-benzothiophene-3-carboxamide; PknG Inhibitor ; |
| CAS号 | 329221-38-7 |
| Inchi | InChI=1S/C13H16N2O2S/c14-11(16)10-8-3-1-2-4-9(8)18-13(10)15-12(17)7-5-6-7/h7H,1-6H2,(H2,14,16)(H,15,17) |
| InchiKey | VATFNEMGBRWLHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| 分子式 Formula | C13H16N2O2S |
| 分子量 Molecular Weight | 264.34 |
| 溶解度Solubility | 生物体外In Vitro:DMSO溶解度≥ 32 mg/mL(121.06 mM)*"≥" means soluble可溶, but saturation unknown溶解度未知. |
| 性状 | 浅褐色固体粉末,Power |
| 储藏条件 Storage conditions | -20°C 3 years年 4°C 2 years年 / In solvent溶液中:-80°C 6 months月 -20°C 1 month月 |
PknG抑制剂(AX20017,329221-38-7)实验注意事项:
1.实验前需戴好防护眼镜,穿戴防护服和口罩,佩戴手套,避免与皮肤接触。
2.实验过程中如遇到有毒或者刺激性物质及有害物质产生,必要时实验操作需要手套箱内完成以免对实验人员造成伤害
3.实验后产生的废弃物需分类存储,并交于专业生物废气物处理公司处理,以免造成环境污染Experimental considerations:
1. Wear protective glasses, protective clothing and masks, gloves, and avoid contact with the skin during the experiment.
2. The waste generated after the experiment needs to be stored separately, and handed over to a professional biological waste gas treatment company to avoid environmental pollution.
Tags:AX20017试剂,AX20017杂质,AX20017合成,AX20017中间体,AX20017密度,AX20017溶解度,AX20017旋光度,AX20017闪点,AX20017熔点,AX20017购买,

| 产品说明 | PknG抑制剂(AX20017,329221-38-7)是蛋白激酶G (PknG) 的小分子的抑制剂,IC50值是 0.39 μM |
| Introduction | PknG抑制剂(AX20017,329221-38-7) is a smallolecule protein kinase G (PknG) inhibitor with anIC50of 0.39 μM. |
| Application1 | |
| Application2 | |
| Application3 |
PknG抑制剂(AX20017,329221-38-7)是一种细胞可渗透的四氢苯并噻吩化合物,可作为针对分枝杆菌蛋白激酶G(PknG; IC 50 = 390 nM)的高度特异性和ATP结合位点靶向抑制剂,而对其他8种分枝杆菌和25种其他人类细胞则无活性降低或无活性激酶,包括与PknG关系最密切的哺乳动物激酶PKCα。已显示AX20017可以完全灭活PknG介导的溶酶体转移阻滞和巨噬细胞中牛分枝杆菌 BCG的降解(浓度为10μM或更高),否则不会影响BCG在其感染宿主外的生长。
| 警示图 | |
| 危险性 | warning |
| 危险性警示 | Not available |
| 安全声明 | H303吞入可能有害+H313皮肤接触可能有害+H2413吸入可能对身体有害 |
| 安全防护 | P264处理后彻底清洗+P280戴防护手套/穿防护服/戴防护眼罩/戴防护面具+P305如果进入眼睛+P351用水小心冲洗几分钟+P338取出隐形眼镜(如果有)并且易于操作,继续冲洗+P337如果眼睛刺激持续+P2393获得医疗建议/护理 |
| 备注 | 实验过程中防止吸入、食入,做好安全防护 |
| Walburger A, et al. Protein kinase G from pathogenic mycobacteria promotes survival within macrophages. Science. 2004 Jun 18;304(5678):1800-4. |
| Santhi N, et al. Insights from the molecular docking of withanolide derivatives to the target protein PknG from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Bioinformation. 2011;7(1):1-4. |
| Scherr N, et al. Structural basis for the specific inhibition of protein kinase G, a virulence factor of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jul 17;104(29):12151-6. |
1、Insights from the molecular docking of withanolide derivatives to the target protein PknG from Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Natchimuthu Santhi 1, Sekar Aishwarya
Abstract A crucial virulence factor for intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis survival is Protein kinase G (PknG), a eukaryotic-like serinethreonine protein kinase expressed by pathogenic mycobacteria that blocks the intracellular degradation of mycobacteria in lysosomes. Inhibition of PknG results in mycobacterial transfer to lysosomes. Withania somnifera, a reputed herb in ayurvedic medicine, comprises a large number of steroidal lactones known as withanolides which show various pharmacological activities. We describe the docking of 26 withanferin and 14 withanolides from Withania somnifera into the three dimensional structure of PknG of M. tuberculosis using GLIDE. The inhibitor binding positions and affinity were evaluated using scoring functions- Glidescore. The withanolide E, F and D and Withaferin - diacetate 2 phenoxy ethyl carbonate were identified as potential inhibitors of PknG. The available drug molecules and the ligand AX20017 showed hydrogen bond interaction with the aminoacid residues Glu233 and Val235. In addition to Val235 the other amino acids, Gly237, Gln238 and Ser239 are important for withanolide inhibitor recognition via hydrogen bonding mechanisms.
2、Predictive Binding Affinity of Plant-Derived Natural Products Towards the Protein Kinase G Enzyme of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ( Mt PknG)
Rana M Qasaymeh 1, Dino Rotondo 1, Carel B Oosthuizen 2, Namrita Lall 2 3 4, Veronique Seidel
Abstract Tuberculosis (TB), caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, is a growing public health concern worldwide, especially with the emerging challenge of drug resistance to the current drugs. Efforts to discover and develop novel, more effective, and safer anti-TB drugs are urgently needed. Products from natural sources, such as medicinal plants, have played an important role in traditional medicine and continue to provide some inspiring templates for the design of new drugs. Protein kinase G, produced by M. tuberculosis (MtPKnG), is a serine/threonine kinase, that has been reported to prevent phagosome-lysosome fusion and help prolong M. tuberculosis survival within the host's macrophages. Here, we used an in silico, target-based approach (docking) to predict the interactions between MtPknG and 84 chemical constituents from two medicinal plants (Pelargonium reniforme and Pelargonium sidoides) that have a well-documented historical use as natural remedies for TB. Docking scores for ligands towards the target protein were calculated using AutoDock Vina as the predicted binding free energies. Ten flavonoids present in the aerial parts of P. reniforme and/or P. sidoides showed docking scores ranging from -11.1 to -13.2 kcal/mol. Upon calculation of all ligand efficiency indices, we observed that the (-?G/MW) ligand efficiency index for flavonoids (4), (5) and (7) was similar to the one obtained for the AX20017 control. When taking all compounds into account, we observed that the best (-?G/MW) efficiency index was obtained for coumaric acid, coumaraldehyde, p-hydroxyphenyl acetic acid and p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol. We found that methyl gallate and myricetin had ligand efficiency indices superior and equal to the AX20017 control efficiency, respectively. It remains to be seen if any of the compounds screened in this study exert an effect in M. tuberculosis-infected macrophages.
3、Structural basis for the specific inhibition of protein kinase G, a virulence factor of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Nicole Scherr 1, Srinivas Honnappa, Gabriele Kunz, Philipp Mueller, Rajesh Jayachandran, Fritz Winkler, Jean Pieters, Michel O Steinmetz
Abstract The pathogenicity of mycobacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis is closely associated with their capacity to survive within host macrophages. A crucial virulence factor for intracellular mycobacterial survival is protein kinase G (PknG), a eukaryotic-like serine/threonine protein kinase expressed by pathogenic mycobacteria that blocks the intracellular degradation of mycobacteria in lysosomes. Inhibition of PknG with the highly selective low-molecular-weight inhibitor AX20017 results in mycobacterial transfer to lysosomes and killing of the mycobacteria. Here, we report the 2.4 A x-ray crystal structure of PknG in complex with AX20017. The unique multidomain topology of PknG reveals a central kinase domain that is flanked by N- and C-terminal rubredoxin and tetratrico-peptide repeat domains, respectively. Directed mutagenesis suggests that the rubredoxin domain functions as a regulator of PknG kinase activity. The structure of PknG-AX20017 further reveals that the inhibitor is buried deep within the adenosine-binding site, targeting an active conformation of the kinase domain. Remarkably, although the topology of the kinase domain is reminiscent of eukaryotic kinases, the AX20017-binding pocket is shaped by a unique set of amino acid side chains that are not found in any human kinase. Directed mutagenesis of the unique set of residues resulted in a drastic loss of the compound's inhibitory potency. Our results explain the specific mode of action of AX20017 and demonstrate that virulence factors highly homologous to host molecules can be successfully targeted to block the proliferation of M. tuberculosis.
4、A novel drug discovery concept for tuberculosis: inhibition of bacterial and host cell signalling
Rita Székely 1, Frigyes Wáczek, István Szabadkai, Gábor Németh, Bálint Hegymegi-Barakonyi, Dániel Eros, Bálint Szokol, János Pató, Doris Hafenbradl, Jacqueline Satchell, Brigitte Saint-Joanis, Stewart T Cole, László Orfi, Bert M Klebl, György Kéri
Abstract The Mycobacterium tuberculosis genome encodes for eleven eukaryotic-like Ser/Thr protein kinases. At least three of these (PknA, PknB and PknG) are essential for bacterial growth and survival. PknG is secreted by pathogenic mycobacteria, in macrophages to intervene with host cell signalling pathways and to block the fusion of the lysosomes with the phagosome by a still unknown mechanism. Based on our previously published results, we have initiated a drug discovery program, aiming to improve the potency against PknG and the physiochemical properties of the initially identified hit compound, AX20017, from the class of the tetrahydrobenzothiophenes. We have established a radioactive biochemical PknG kinase assay to test the novel analogues around AX20017. We have developed lead molecules with IC50 values in nanomolar range, and demonstrated their antituberculotic effects on human macrophages. Selected leads might ultimately serve the purpose of inducing phagosomal-lysosomal fusion and therefore destroy the residence of the intracellular mycobacteria. It is unclear at this time if these "homeless" mycobacteria are getting killed by the host, but they will be at least vulnerable to the activity of antimycobacterial agents. Released mycobacteria rely on the essential function of PknB for survival, which is our second molecular kinase target. PknB is a transmembrane protein, responsible for the cell growth and morphology. We have screened our library and synthesized novel compounds for the inhibition of PknB. A pharmacophore model was built and 70,000 molecules from our synthesizable virtual library have been screened to identify novel inhibitor scaffolds for the generation of templated compound libraries. Currently, we are using a radioactive kinase assay employing GarA as the putative, physiological substrate of PknB kinase. We have identified hits and generated optimised hit compounds with IC50 values for the inhibition of PknB in the nanomolar range. Yet those promising hits are not potent enough to yield meaningful "minimum inhibitory concentrations" in mycobacterial growth assays. In the course of our future work, we will increase the potency of the next generation of PknB inhibitors in order to improve their antibacterial activity.
- 相关产品
-
< >
- 推荐产品
-
< >
- 最新产品
-
< >
新闻
怎么做细胞爬片免疫组化染色实验
细胞爬片免疫组化染色,是通过细胞爬片是让玻片浸在细胞培养基内,细胞在玻片上生长,主要用于组织学,免疫组织化学...
2020/7/20 22:04:33
提取病毒RNA的实验方法
提取病毒RNA方法分别有:异硫氰酸胍的提取病毒RNA方法、TRIzol LS提取法、Trizol法提取法等等...
2020/7/22 20:29:26

chelex 100树脂国产替代之路-BIOFOUNT范德生物
Chelex 100螯合离子交换树脂对铜、铁和其他重金属?的偏好显著高于对钠、钾等一价阳离子的偏好。它对二价...
2025/11/4 14:22:46

9月开学季——助研新学期 范德送好礼
2025/8/28 15:30:55

Waxfilm 实验室封口膜:技术与国际市场的双重突破
在实验室耗材领域,封口膜是保障实验准确性与稳定性的关键产品之一。近年来,Waxfilm?实验室封口膜凭借其卓...
2025/5/13 13:03:40

Waxfilm实验室封口膜的5大突破
Waxfilm实验室封口膜作为生物功能膜领域的国产技术突破和品牌突破,是生物领域中国技术发展的缩影。
2025/5/6 17:02:07
各种微流控芯片键合方法的优缺点
微流控芯片键合:目前主要有激光焊接、热压键合、胶键合、超音波焊接,每种方法都有各自的优缺点。本文主要介绍聚酯...
2023/7/28 10:43:09

新一代微流控键合解决方案
微流控键合解决方案:微流控芯片制造的一个重要环节,也是最容易被忽视的--芯片键合。其中一个重要因素是:微流控...
2023/7/27 12:44:28
荧光素钾盐使用说明
D-荧光素钾盐(K+)设计用于体外和体内生物发光测定。D-荧光素的质量和纯度对于获得良好和可重复的结果至关重...
2023/7/20 11:05:11
如何选BSA(牛血清白蛋白)
如何选BSA(牛血清白蛋白):牛血清白蛋白(BSA)有多种形式,如何选择适合自己的牛血清白蛋白(BSA)是一...
2023/2/14 13:09:18




 购物车
购物车 



